Canvas2D mobile web game 开发– 实现
PUBLISHED
简介
在阅读本文之前,建议你先熟悉“Canvas2D移动web游戏开发 – 基础” ,连同game loop概念介绍了Canvas 2D API。 我们也简要描述一个基本的网页游戏架构。 这里提供示例应用程序 - 地球卫士-的类图。 这就是为什么我们推荐你先从之前的文章开始。
在本文中,我们将专注于实现方面。 我们会详细告诉你游戏图元如何构建,如何把它们整合在一起并放在一个游戏板上。 我们也将解释如何创建一个灵活的等级展示。 作为一个示例应用程序,我们将使用地球卫士1.0.3。
游戏的基本类型
在游戏模组(./js/modules/game.js)中定义有定义不同类型的游戏图元。
var objectTypes = {
PLAYER : 1,
PLAYER_MISSILE : 2,
ENEMY : 4,
ENEMY_MISSILE : 8,
STAR : 16,
EARTH : 32,
HUD : 64,
POWER_UP : 128,
MSG : 256,
OVERHEAT : 512
};我们这样做是为了区分图元代表的图形表示。 由于这种方法,我们可以很容易地计算当前面板上给定类型的图元数量,或者定义给定类型的图元与其他类型图元碰撞。 GameBoard类严重依赖上述对象类型。
GameBoard 类
GameBoard类(./js/classes/GameBoard.js)是聚集一个游戏界面中多个项目的容器类。 在一些游戏框架中这个容器也称为场景。 如果我们的游戏结构中在同一时间只有一个GameBoard 对象可以显示。 这种方法简化了实现。 下面你可以看到GameBoard 对象只会聚合Sprite 对象实例和从Sprite类继承来的类。
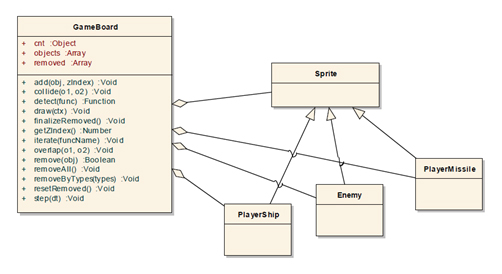
图 1:GameBoard 类图
GameBoard 类的作用
- 将图元整合到一个游戏界面。
- 通过一个类型处理图元数量。 可以通过调用下面的方法请求每个图元类型的对象个数(这种情况下我们知道提供了多少PLAYER 对象):
someBoard.cnt[game.getObjectTypes().PLAYER]
- 添加对象时,图元Z轴索引的管理。 zIndex设置的越低,图元显示的就越低。 当你设置某些对象zIndex为0时,他们会被zIndex更大的图元覆盖。 为了更好的理解zIndex的概念,请参考下面的代码和图片。
someBoard.add(somePrimitive, zIndex)

图 2:GameBoard zIndex概念。 导弹具有最高的zIndex,HUD和地球稍微低一点,敌人和玩家的飞船zIndex最低。
- 从board中移除所有的图元
someBoard.removeAll()
- 移除特定类型的图元
someBoard.removeByTypes(game.getObjectTypes().PLAYER)
- 迭代一个给定board上的所有图元。 如果你调用board的迭代方法,所有集合的图元渲染方法都会被调用。 值得注意的是draw是一个特殊的方法,因为通常drawUnder在它之前调用,drawOver在它之后调用。 后面会介绍为什么这样。
someBoard.iterate(“draw”)
- 图元之间的碰撞检测 下面的例子中,我们检测给定的enemy对象和任意玩家导弹之间的第一个碰撞。 对于第一个碰撞,我的意思是,在一个游戏循环迭代中只检测到一个冲突,即使许多导弹和敌人重叠。
someBoard.collide(enemy, game.getObjectTypes().PLAYER_MISSILE)

图 3:同一时刻只有一个GameBoard 对象可以显示
Sprite 类
Sprite 类定义在 ./js/classes/Sprite.js ,它的主要目的是使用spriteSheet模块(请参考前面的文章:Canvas2D移动web游戏开发 – 基础 获取更多关于sprite处理的信息),来渲染游戏图元。 每一个游戏图元,例如Enemy,PlayerShip和Explosion等。 从Sprite类继承而来。 下面有Sprite类功能的简短描述:
- 从spriteSheet模块恢复相关给定Sprite的数据,例如宽,高,帧数等。
- 使用spriteSheet的draw函数来物理渲染图元。
- 为从Sprite中继承并重载的drawUnder和drawOver方法定义桩。 这些方法的主要目的是提供在给定sprite之上或者下面去渲染图形的可能。 这不是一个替代GameBoard的z-index值的机制,而是一个额外的功能。
在我们的示例应用程序中有Sprite类没有定义的实例。 在这个工程里Sprite是一个抽象类。
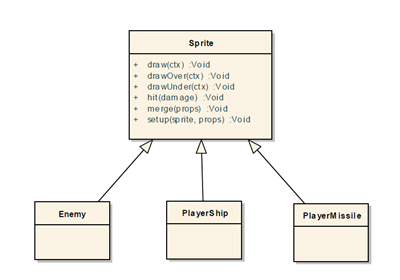
图 4:Sprite类图
图元设计示例 - PlayerMissile
继承Sprite类的每个图元需要一个类型定义。 我们必须提供一个总是在调用draw之前调用game loop的方法的实现(更多game loop信息,请参考:Canvas2D mobile web game development – basics)。 方法总是用来计算新的图元位置。 传递给每一个方法的唯一参数称为dt。 这个参数是非常重要的,因为它是用在所有的运动方程通过游戏加快或减慢的运动。 请参考下面的代码PlayerMissile类:
"use strict";
var PlayerMissile = function(x, y) {
this.type = game.getObjectTypes().PLAYER_MISSILE;
this.setup('missile', {
damage : 10
});
this.x = x - this.w / 2;
// Use the passed in y as the bottom of the missile
this.y = y - this.h;
// y velocity of Player Missile
this.vy = -700;
/**
* Function: - change the y position of the missile, - checks if the PlayerMissile isn't outside the board (if yes - removes the missile), - checks if the PlayerMissile collides with Enemy,
*
* @param dt
*/
this.step = function(dt) {
this.y += this.vy * dt;
if (this.y < config.player.topOffset) {
this.board.remove(this);
}
var collision = this.board.collide(this, game.getObjectTypes().ENEMY);
if (collision) {
collision.hit(this.damage);
this.hit();
}
};
/**
* Function defines how collision with other object affects the PlayerMissile (it destroys the missile and removes it from board)
*/
this.hit = function() {
this.board.add(new Explosion(this.x + this.w / 2, this.y + this.h, "explosion_yellow_small"), 100);
this.board.remove(this);
}
};
game.inherit(PlayerMissile, Sprite);你可以看到,在步骤方法的第一行是:this.y += this.vy * dt;
下面的等式中的T是game loop的周期 - 更多细节在“Canvas2D mobile web game development – basics”中解释。
这里有一个Y轴的运动等式,dt参数被定义在game module(./js/game.js),dt = T/1000。 在我们的例子中T=2500, 所以 dt = 2.5。 我们可以这样写运动方程如下:
V(n+1) = V(n) – 700 * 2.5 = V(n) – 1750
如果我们增加game周期(减少FPS),每个运动等式中的dt需要增加,因为我们需要移动对象。 dt参数容许我们平滑改变game FPS,不影响用户看到的图元速度。
Enemy 类
enemy 类提供游戏中enemy图元的实现。 它定义了什么是enemy对象和enemy的运动等式的参数的冲突的可能。
没一个enemy 对象是用两个运动等式描述。
Vx(t)= A + B * sin(C*t+D)
Vy (t)= E + F * sin(G*t+H)
请参考下面的两个图片,显示了上述等式的图形。
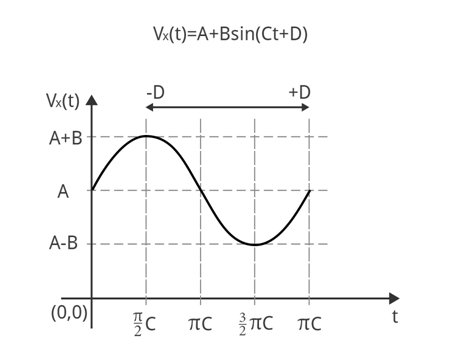
图 5:Vx(t)运动等式
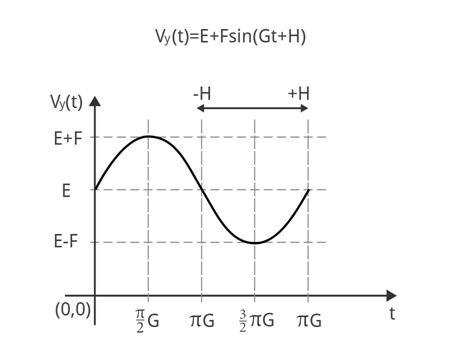
图 6:Vy(t) 运动等式
默认情况下,各个参数的运动方程是等于0。 你可以根据需要重写很多参数,创建更多运动等式。 在enemy类,step方法是用于计算enemy的新位置 - 定义两个运动等式。
/**
* Function changes the position and velocity of Enemy, fires missile
* @param dt
*/
this.step = function(dt) {
this.t += dt;
this.vx = this.A + this.B * Math.sin(this.C * this.t + this.D);
this.vy = this.E + this.F * Math.sin(this.G * this.t + this.H);
this.x += this.vx * dt;
this.y += this.vy * dt;
if (this.reload <= 0 && Math.random() < this.firePercentage) {
this.reload = this.reloadTime;
if (this.missiles == 2){
this.board.add(new EnemyMissile(this.x, this.y + this.h), 100);
this.board.add(new EnemyMissile(this.x + this.w, this.y + this.h), 100);
} else {
this.board.add(new EnemyMissile(this.x + this.w / 2, this.y + this.h), 100);
}
}
this.reload -= dt;
};Enemy 类型
在地球保卫应用中,有多个不同类型的enemy - 请参考./js/config.js 文件。 下面解释的基础enemy配置提供每个定义可以重写。
var enemies = {
/**
* Attributes of enemy:
* x - initial position (this will be multiplied by a random factor)
* sprite - sprite of enemy
* A - constant horizontal velocity
* B - strength of horizontal sinusoidal velocity
* C - period of horizontal sinusoidal velocity
* D - time shift of horizontal sinusoidal velocity
* E - constant vertical velocity
* F - strength of vertical sinusoidal velocity
* G - period of vertical sinusoidal velocity
* H - time shift of vertical sinusoidal velocity
* health - number of hits needed to kill the enemy
* damage - damage done to the PlayerShip object
* missiles - number of missiles to fire by enemy
* firePercentage - percent of the missiles to be accually fired
* pointsHit - points added for hitting the enemy by player
* pointsDestroy - points added for destroying the enemy by player
*/
basic : {
x : 100,
sprite : 'enemy_purple',
B : 100,
C : 2,
E : 100,
health : 30,
damage : 10,
missiles : 2,
firePercentage : 0.003,
pointsHit : 15,
pointsDestroy : 60
},
straight : {
x : 100,
sprite : 'enemy_ship',
E : 200,
health : 30,
damage : 10,
firePercentage : 0.001,
pointsHit : 10,
pointsDestroy : 40
},
…enemy定义和可视化示例
下面我们提供地球保卫游戏的第四层的level定义的一部分。
types : [ {
basicType : enemies.basic,
overrides : {
x : 350,
B : 200,
C : 1,
E : 55,
firePercentage : 0.008
}
} ],
Y速度: Vy(t) = 55。 这意味着敌人会具有恒定的时间Y速度等于55。 enemy的运动Vx(t)=0是可视的。

图 7:Vy(t)=55 with Vx(t)=0
如果我们添加X速度等于Vx(t)=200*sin(t),运动将会改成正弦曲线,如下图所示。
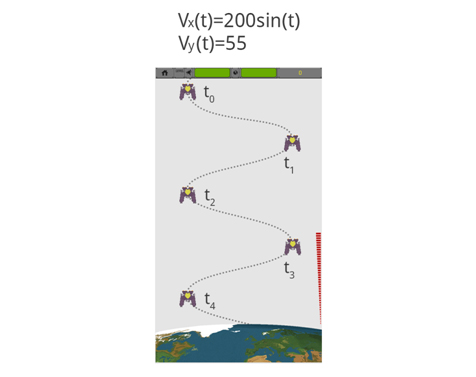
图 8:Vy(t)=55 with Vx(t)=200*sin(t)
Levels 实现
如果你想你的游戏更多吸引人的地方,你需要想到许多不同的level。 从一个开发者角度每个级别应该以一致的方式来定义。 你应该提供开始,停止和转换level的机制。 如果地球卫士的每一层是由时间限制。 这意味着level将结束,无论显示或杀死敌人的数目。 可以在下面找到描述每个level的参数(参考./js/config.js):
{
period : 2300, //
// Array with enemies that will be displayed very "period" time
// In this case 2 enemies will be displayed each 2300msec.
types : [ {
basicType : enemies.straight, // basic enemy type
overrides : { // all motion parameters can be overridden here
x : 650,
E : 45
}
}, {
basicType : enemies.basic,
overrides : {
x : 400,
B : 100,
C : 1,
E : 60
}
} ],
duration : 90, // level duration in seconds
name : "Tighter...", // level name
powerUps : {
number : 3 // number of power ups that will be displayed during the level
}除了level定义和实现,你需要level管理机制。 levelManager应运而生 - ./js/modules/levelManager.js。 提供以下方法:
- 启动某一级别
- 停止某一级别
- 获取级别阵列
- 获取当前处理级别
- 获取已经通过的级别
- 存储已经通过的关卡
参考以下代码。
"use strict";
var levelManager = function() {
var levels = [];
var alreadyPassedLevels = [];
for ( var i = 0; i < config.levels.length - 1; i += 2) {
var nextLevel = new Level(config.levels[i + 1]);
nextLevel.num = i + 2;
var thisLevel = new Level(config.levels[i]);
thisLevel.num = i + 1;
thisLevel.options.nextLevel = nextLevel;
if (levels[i - 1])
levels[i - 1].options.nextLevel = thisLevel;
levels.push(thisLevel);
levels.push(nextLevel);
}
return {
init : function() {
if (localStorage.getItem('levels')) {
alreadyPassedLevels = $.parseJSON(localStorage.getItem('levels'));
}
},
/**
* Starts given level
*
* @param {Number} number
* @returns {Boolean} true in case of success
*/
start : function(number) {
if (typeof levels[number - 1] === "undefined") {
game.log("ERROR: Unable to find level " + number);
return false;
} else {
var currLevel = this.getCurrentLevel();
if (currLevel)
currLevel.stop(true);
levels[number - 1].start();
return true;
}
},
/**
* Returns all levels
*
* @returns
*/
getLevels : function() {
return levels;
},
/**
* Returns current active level
*
* @returns
*/
getCurrentLevel : function() {
for ( var i = 0; i < levels.length; i++) {
if (levels[i].isRunning())
return levels[i];
}
return false;
},
/**
* Method to force stop current level
*
* @returns
*/
stopCurrentLevel : function() {
var cl = levelManager.getCurrentLevel();
if (cl) {
cl.stop(true);
}
},
/**
* Stores already passed level in localStorage
*
* @param level
* @returns
*/
storePassedLevel : function(level) {
if (alreadyPassedLevels.indexOf(level.num) === -1) {
alreadyPassedLevels.push(level.num);
localStorage.setItem('levels', JSON.stringify(alreadyPassedLevels));
game.log("adding level");
} else {
game.log("not adding level");
}
},
/**
* Gets the levels that the player has already passed during previous games.
*
* @returns {Array} numbers of already passed levels
*/
getAlreadyPassedLevels : function() {
var alreadyPassed = $.parseJSON(localStorage.getItem('levels'));
if (!alreadyPassed)
alreadyPassed = [];
if (config.allLevelsVisible) {
var alreadyPassed = [];
for ( var i = 1; i <= this.getLevels().length; i++) {
alreadyPassed.push(i);
}
}
return alreadyPassed;
}
}
}();总结
本文中,我们描述了Tizen平台手机web游戏的示例实现。 现在你知道GameBoard类代表的主要意义,如何定义游戏图元,如何处理关卡。 本文很容易在其他手机web游戏开发再利用,而不需要任何游戏框架。
