CVE check for open source
PUBLISHED
1 Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures(CVE) check overview for open source
- Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE)
- CVE is a dictionary of common names for publicly known cyber security vulnerabilities. CVE's common identifiers make it easier to share data across separate network security databases and tools, and provide a baseline for evaluating the coverage of an organization’s security tools.
- If you have more information, please refer following url: https://cve.mitre.org/about/
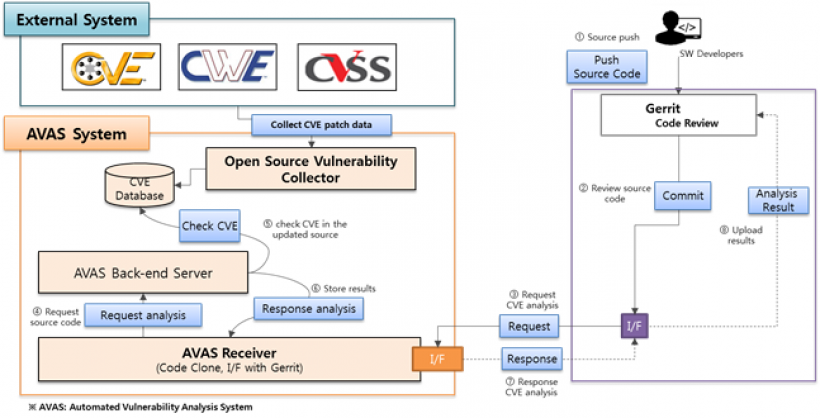
- AVAS (Automated Vulnerability Analysis System) Tool
- The potential security defects for open source can be prevented using AVAS tool at the Code Review Stage.
- All developers have to review the potential defect.
- True Alarm : modify the relevant code and make new patch set
- False Alarm : upload the JIRA ignore request post
2 How to use CVE Check in Gerrit
You can modify the potential security defects through the following methods in gerrit.
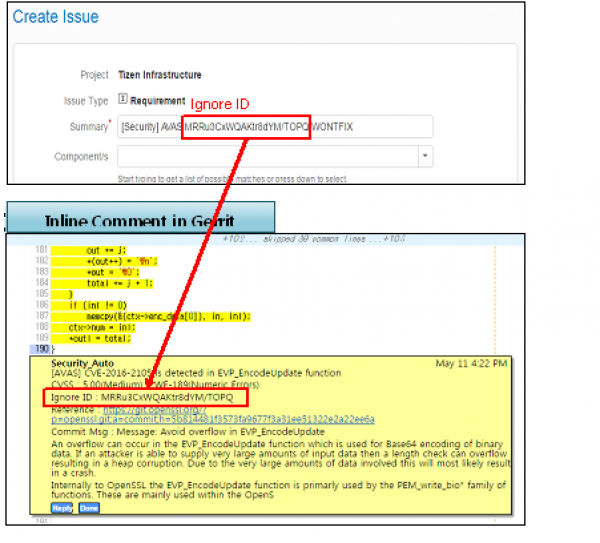
- Inline Comment
- You can see the potential security defects in inline comment.
- There is shown the patch url you need to check and you can refer the patched source code by clicking this.
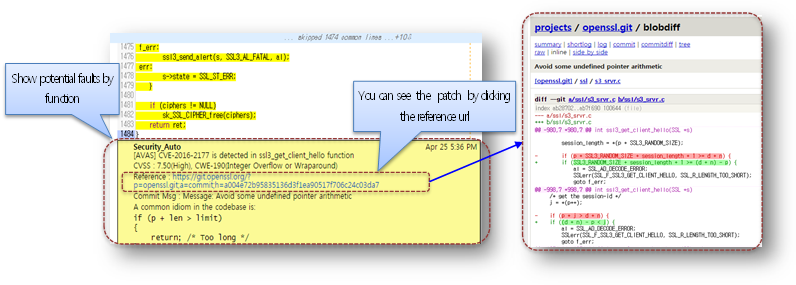
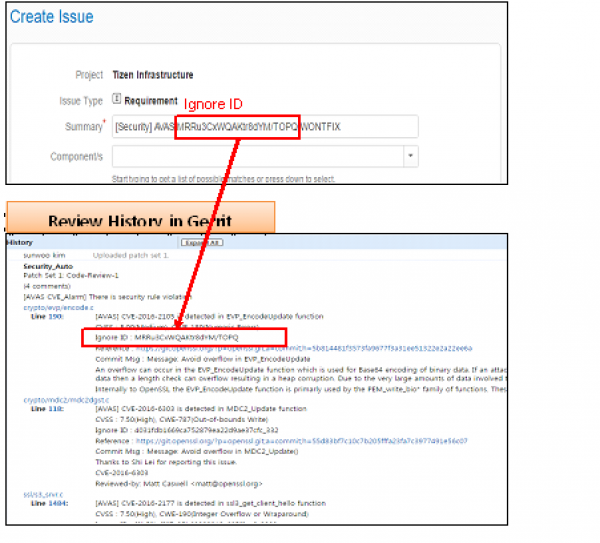
- Review History
- You can also see the potential security defects in review history.
- It displays the patch information that including the line number, commit message, reference link, security level and so on.
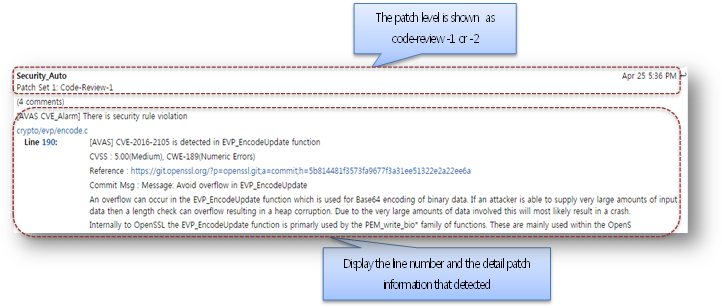
3 Jira Ignore Request Process
- Connect to https://bugs.tizen.org/projects/TINF
- Login with Tizen account
- Click ‘Create’

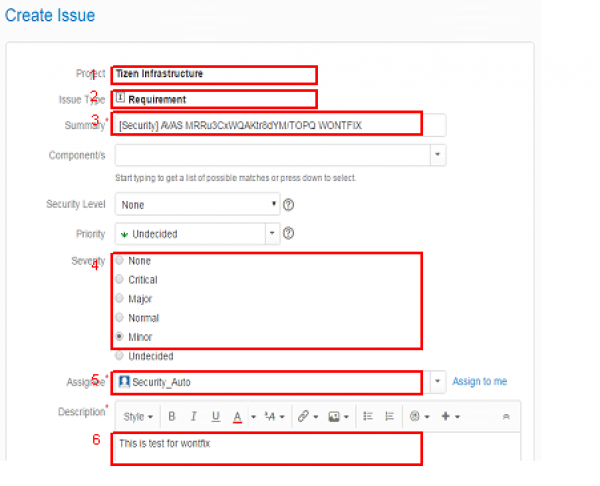
- Fill the request form using below guideline.
- Project : Tizen Infrastructure(TINF)
- Issue Type : Requirement
- Summary : [Security] AVAS [Ignore ID] [WONTFIX / FALSEPOSITIVE]
- Severity : Choose the severity of the issue.
- Assignee : Security_Auto (avas.swc@samsung.com)
- Description : Write the reason why this warning should be ignored
|
Classification |
Description |
|
WONTFIX |
The warnings that are not making trouble |
|
FALSEPOSITIVE |
The warning might be a defect according to the program language, but it will not make trouble in this code |
- You can find the Ignore ID in Inline Comment and Review History as below
- Security_Auto can process your ignore request within 10 minutes.
- After your request is done, status of JIRA is changed to “RESOLVED” and Security_Auto writes the comment within 10 minutes.
- After that, AVAS don’t check the same warnings.
- Status : RESOLVED
- Comments : Add a comment regarding warning
- Severity
You can decide the priority of each flaw according to your opinion.
|
Classification |
Criteria |
|
Critical |
- Vulnerabilities enabling root, system and shell privilege - Remote privileged code execution (at a privileged level) - Local permanent device compromise, which results in un-repairable device without re-flashing the entire OS - Trusted Execution Environment Compromise - Unauthorized local access to protected data(i.e., TrustZone) or capabilities - Remote permanent denial of service, which either results in permanent inoperability or requires reflashing the device - Hardware-protected key compromise |
|
High (Major) |
- Remote unprivileged code execution - Unauthorized local access to system/signature-level permission data or capabilities - Local permanent denial of service, which either results in permanent inoperability or requires reflashing the device - Remote temporary denial of service, which causes remote hang or reboot - Software protected key compromises to access system/signature-level permission data or capabilities - Unauthorized network unlock |
|
Medium (Minor) |
- Unauthorized access to personal information or dangerous level permission data or capabilities with an app installed on the device - Local temporary denial of service, which can be resolved only through a factory reset - Software protected key compromises to access dangerous-level permission data or capabilities |
|
Low (Normal) |
- Unauthorized access to normal level permission data or capabilities with an app installed on the device - Local temporary denial of service, which can be resolved by rebooting and removing the problem in Safe Mode - Software protected key compromises to access normal-level permission data or capabilities |